1°) Désactiver SELinux
Editer le fichier /etc/selinux/config
[root@Superlog ~]# vi /etc/selinux/config SELINUX=disabled
2°) Désactiver l’IPV6 (3 nœuds gfsw)
[root@superlog ~]# vi /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv6.conf.all.autoconf = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.autoconf = 0
[root@superlog ~]# sysctl -p
3°) Instalation des packets utiles
[root@superlog ~]# yum -y update && yum -y upgrade [root@superlog ~]# yum -y install epel-release [root@superlog ~]# yum -y install wget locate vim nmap pwgen
4°) Installation JAVA8
[root@superlog ~]# yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headless.x86_64 [root@superlog ~]# java -version

5°) Installation ElasticSearch
Création d’un dépôt ElasticSearch pour l’installation
Importation des certificats GPG signing key ElasticSearch
[root@superlog ~]# rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
[root@superlog ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo [elasticsearch-6.x] name=Elasticsearch repository for 6.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
Installation via le dépôt
[root@superlog ~]# yum -y update && yum install -y elasticsearch
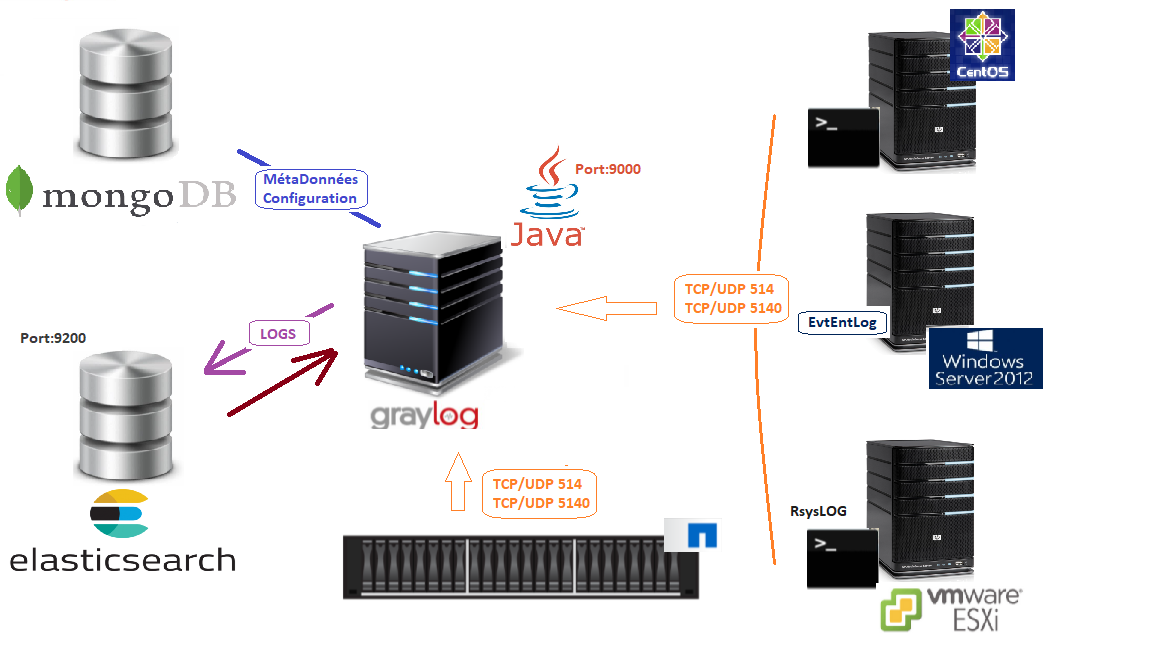
Configuration de ElastiSearch pour notre Cluster
[root@superlog ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Remplacer #cluster.name: my-application
Par
cluster.name: superlog
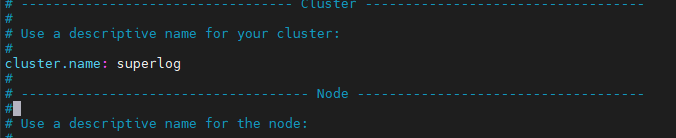
Activer au démarrage le service ElasticSearch
[root@superlog ~]# systemctl enable elasticsearch [root@superlog ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch [root@superlog ~]# systemctl status elasticsearch
Ajout des Rules Firewall Port 9200
[root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9200/tcp --permanent [root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
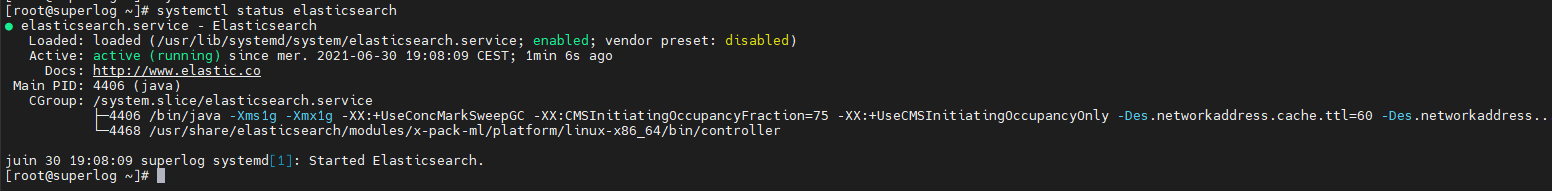
Vérifions que le service travail bien sur le port 9200 du Cluster graylog
[root@superlog ~]# curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
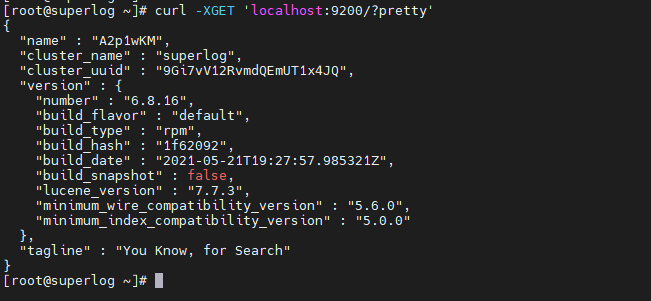
Vérifions l’état de santé du Cluster graylog
[root@superlog ~]# curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true'

6°) Installation MangoDB (BDD)
Création d’un dépôt pour l’installation de la base de données
[root@superlog ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.0.repo [mongodb-org-4.0] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/4.0/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc
Installation du packet
[root@superlog ~]# yum -y update && yum install -y mongodb-org [root@superlog ~]# systemctl enable mongod [root@superlog ~]# systemctl start mongod [root@superlog ~]# systemctl status mongod
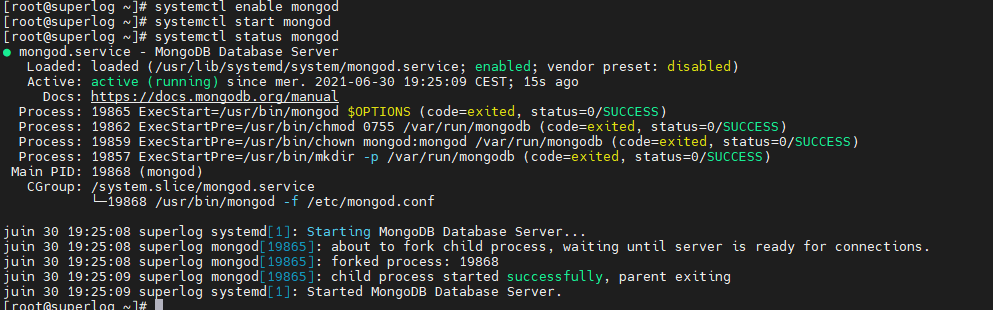
Ajout des Rules Firewall Port 3306
[root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent [root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
7°) Installation GrayLog
Récupère le RPM de GrayLog
[root@superlog ~]# cd /home/chris [root@superlog ~]# rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-3.0-repository_latest.rpm [root@superlog ~]# yum -y update [root@superlog ~]# yum -y install graylog-server
8°) Configurer GrayLog
On va générer un mot de passe via pwgen
[root@superlog ~]# pwgen -N 1 -s 96 AYyqGY7gZPpC0vyhXcF9IL1AvZhLKXJfAXm4P5Ip9xbxMSwPUt1cPc5ySHtIeN0QMyZH0QoqcAdGdxqCOm9nPwSBUoYC0pDA
On va générer un mot de passe pour le compte admin
[root@superlog ~]# echo -n superlog@graylog | sha256sum 8a84e1cfa88315c07c5a22b5aaaac7553c282b82d118cc86c1776e2a0c6aa3d6 -
Editer le fichier de conf de GrayLog
[root@superlog ~]# vi /etc/graylog/server/server.conf #Ajouter ces deux mots de passe fort password_secret = AYyqGY7gZPpC0vyhXcF9IL1AvZhLKXJfAXm4P5Ip9xbxMSwPUt1cPc5ySHtIeN0QMyZH0QoqcAdGdxqCOm9nPwSBUoYC0pDA root_password_sha2 = 8a84e1cfa88315c07c5a22b5aaaac7553c282b82d118cc86c1776e2a0c6aa3d6 root_email = "chris@en-images.info " root_timezone = Europe/Paris elasticsearch_max_docs_per_index = 20000000 elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices = 20 elasticsearch_shards = 1 elasticsearch_replicas = 0 http_bind_address = 192.168.1.149:9000
Démarrer au démarrage le server GrayLog
[root@superlog ~]# systemctl enable graylog-server [root@superlog ~]# systemctl daemon-reload [root@superlog ~]# systemctl start graylog-server [root@superlog ~]# systemctl status graylog-server
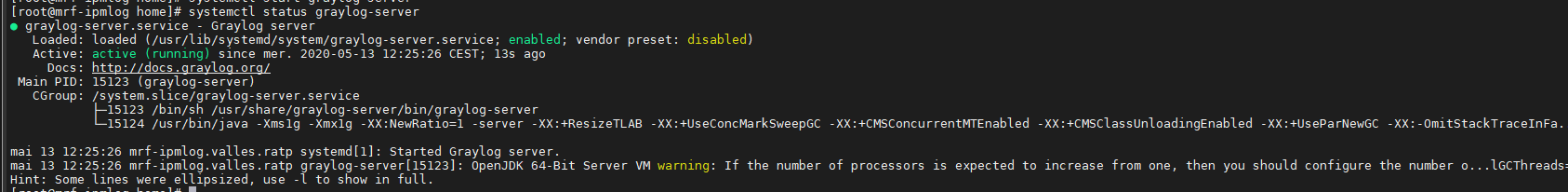
9°) Installer les règles dans Iptables
[root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=http [root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=9000/tcp [root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=5140/udp [root@superlog ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
[root@superlog ~]# tailf /var/log/graylog-server/server.log

10°) Installons Nginx reverse Proxy
[root@superlog ~]# yum -y install nginx
[root@superlog ~]# vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/graylog.conf server { listen 80 default_server; server_name superlog.house.cpb; location / { proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; #proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9000; proxy_pass http://superlog.house.cpb:9000; } }
Edite le fichier nginx.conf et désactiver la conf par défaut
[root@superlog ~]# vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # server { # listen 80 default_server; # listen [::]:80 default_server; # server_name _; # root /usr/share/nginx/html; # Load configuration files for the default server block. # include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; # # location / { # } # error_page 404 /404.html; # location = /40x.html { # } # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # location = /50x.html { # } # }
[root@superlog ~]# systemctl enable nginx [root@superlog ~]# systemctl start nginx [root@superlog ~]# systemctl status nginx
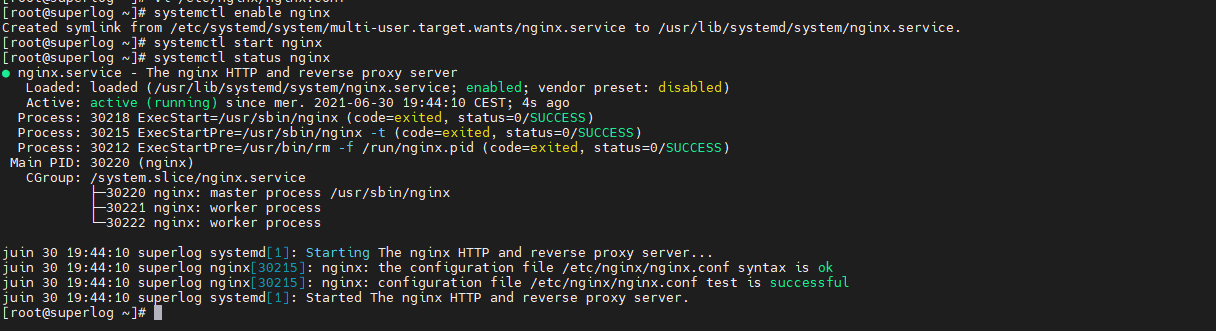
[root@superlog ~]# echo "192.168.1.149 superlog.house.cpb" >> /etc/hosts
Si vous n’avez pas de DNS
- C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts (mode Administrateur)
192.168.1.149 superlog.house.cpb
Connexion à l’interface Web via Firefox ou Chrome
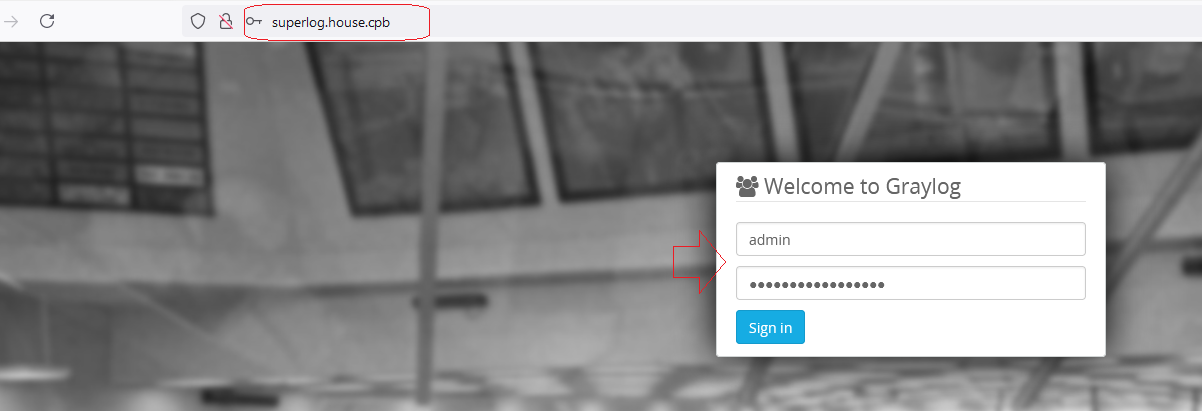
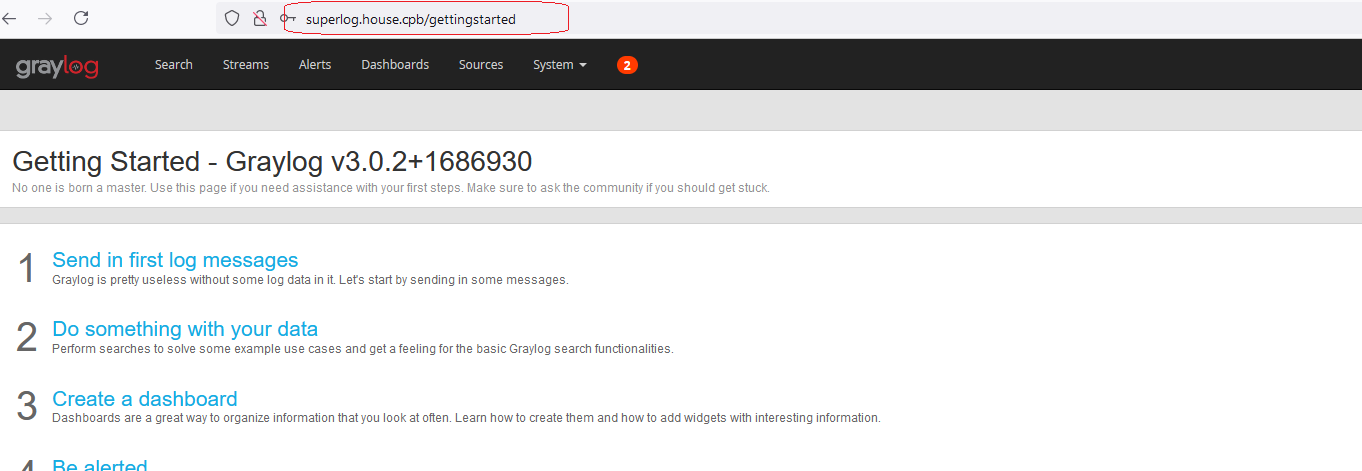
11°) Installation Client de synchronisation de temps
[root@superlog ~]# timedatectl status
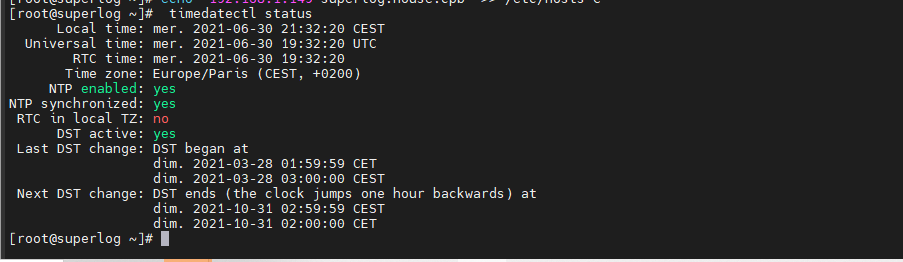
Installation du packet ntp Client via les sources apt
[root@superlog ~]# yum -y install ntp root@Superlog run]# systemctl enable ntpd [root@Superlog run]# systemctl start ntpd
Ajouter les Rules Firewall Port 123 NTP
[root@Superlog run]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ntp [root@Superlog run]# firewall-cmd --reload
Views: 101

